
Nashiry MA, Bhaskar GG, Rice JE (2015) Online testing for three fault models in reversible circuits. International colloquium on automata, languages, and programming.
J Supercomput 71(7):2668–2693īabu HMH, Mia MS, Biswas AK (2017) Efficient techniques for fault detection and correction of reversible circuits. Kotiyal S, Thapliyal H, Ranganathan N (2015) Reversible logic based multiplication computing unit using binary tree data structure.
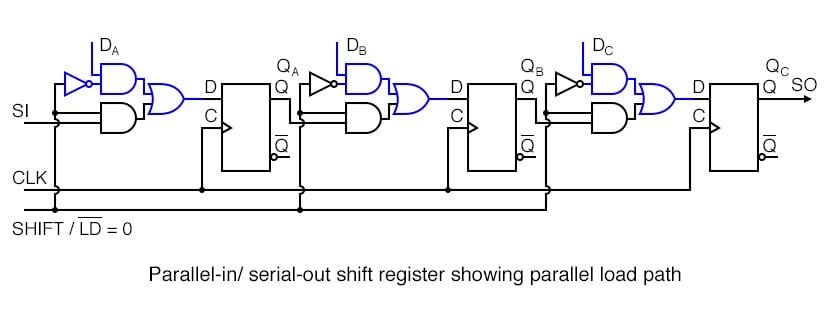
IBM J Res Dev 5(3):183–191īennett CH, Landauer R (1985) The fundamental physical limits of computation. Landauer R (1961) Irreversibility and heat generation in the computing process. The analysis and comparison depict that all new proposed designs have optimized the existing works in terms of performance variables, including quantum cost, number of T gates, and T-depth of the circuit. It has also displayed some efficient designs of the reversible parallel-to-serial converter with parity capability and low-cost design of the control unit for a reversible self-controlled serial adder system. It has been shown that by partial changes in the direct technique, quantum cost and other cost metrics have been improved. This paper has proposed an optimized version of direct feedback technique without any flip-flops and is performed on several samples of reversible circuits design, such as counters and shift registers. There is the principle to look for efficient reversible circuits composed of Clifford + T gates by optimizing quantum cost, the number of T gates, and particularly the T-depth of the circuit, which depends on the type and layout of the reversible gates used in the function. The replacement technique leads to high quantum cost. So far, the direct and replacement techniques have been used in the reversible sequential circuits design. Recently, the synthesis of reversible sequential circuits has attracted researchers’ attention for implementing low-power logic designs.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
